Diagnostic Centre
At Eglinton Healthcare, we offer a full range of non-invasive and minimally invasive cardiac diagnostic tests to help assess, monitor, and manage your heart health. These tests are designed to detect structural or electrical abnormalities of the heart, evaluate its function under rest or stress, and monitor blood pressure or rhythm patterns over time.
Our on-site cardiac diagnostics are conducted by experienced technicians using advanced equipment, often with results reviewed by a cardiologist. Whether you are being screened for heart disease, managing a known cardiac condition, or experiencing symptoms like chest pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath, these tests provide essential information to guide your care.
Diagnostics Tests Available
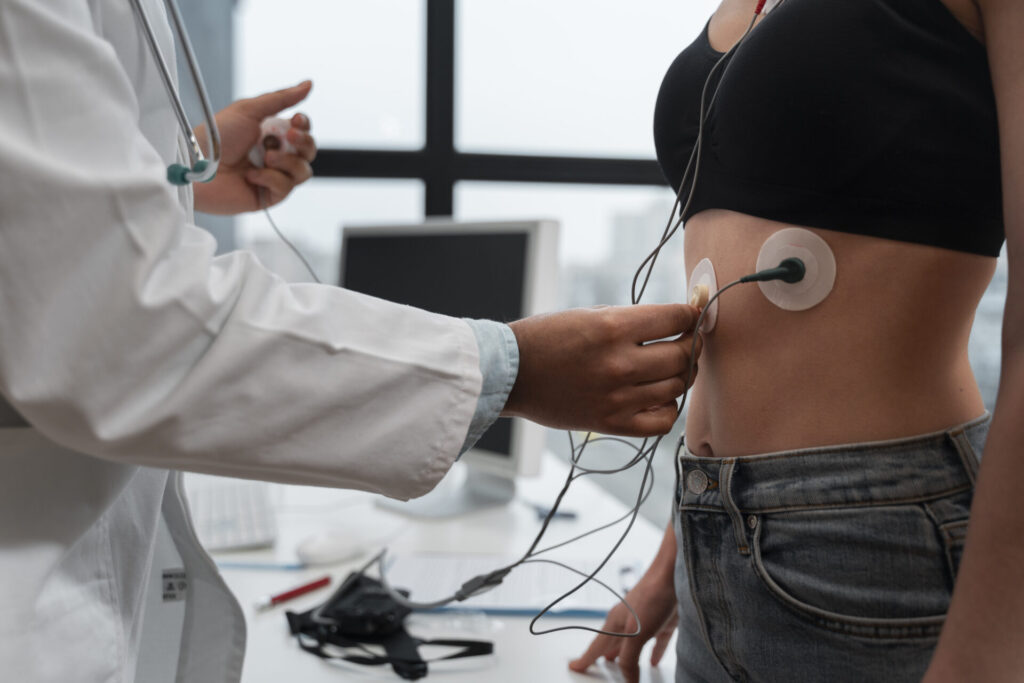
Holter Monitoring

Ambulatory BP Monitoring

INR Instant Testing
Pulmonary Function Tests
EEG/EMG/NCS
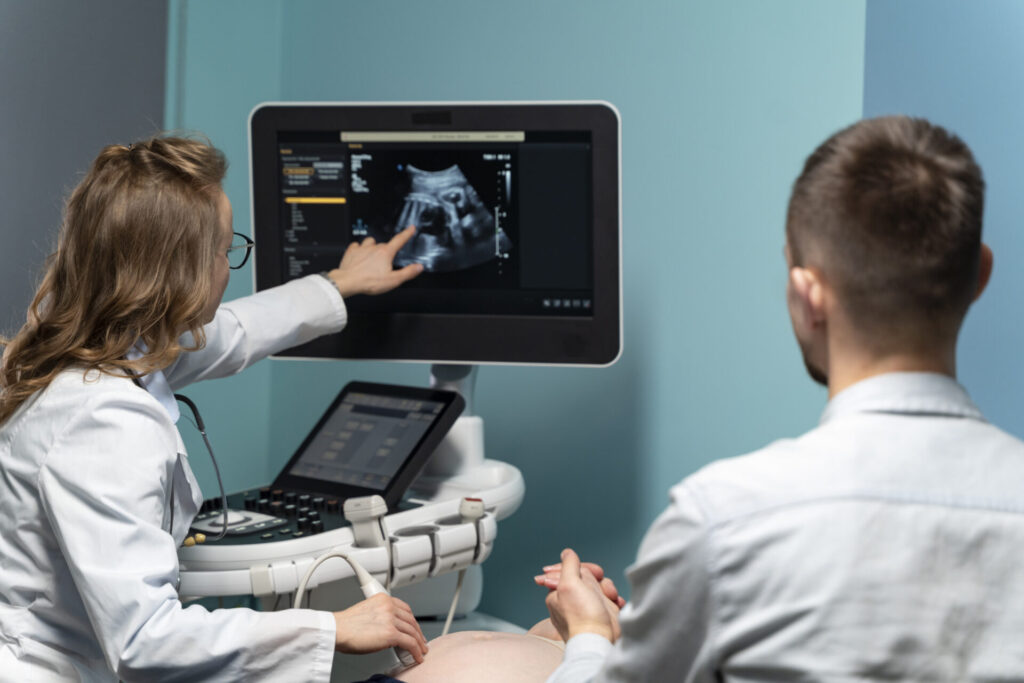
2D Echocardiogram (2D-ECHO)
What it does:
This test uses ultrasound waves to create real-time moving images of your heart, showing how well your heart chambers and valves are working.
What happens during the test:
You will lie on an exam table while a technician applies a small amount of gel to your chest. A handheld device called a transducer is moved over your chest to capture images of your heart. The test is non-invasive and painless.
How to prepare:
No special preparation is needed. You can eat and drink normally and take your medications unless advised otherwise.
What it can diagnose:
Heart valve problems, cardiomyopathy, fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion), and overall heart function (ejection fraction).
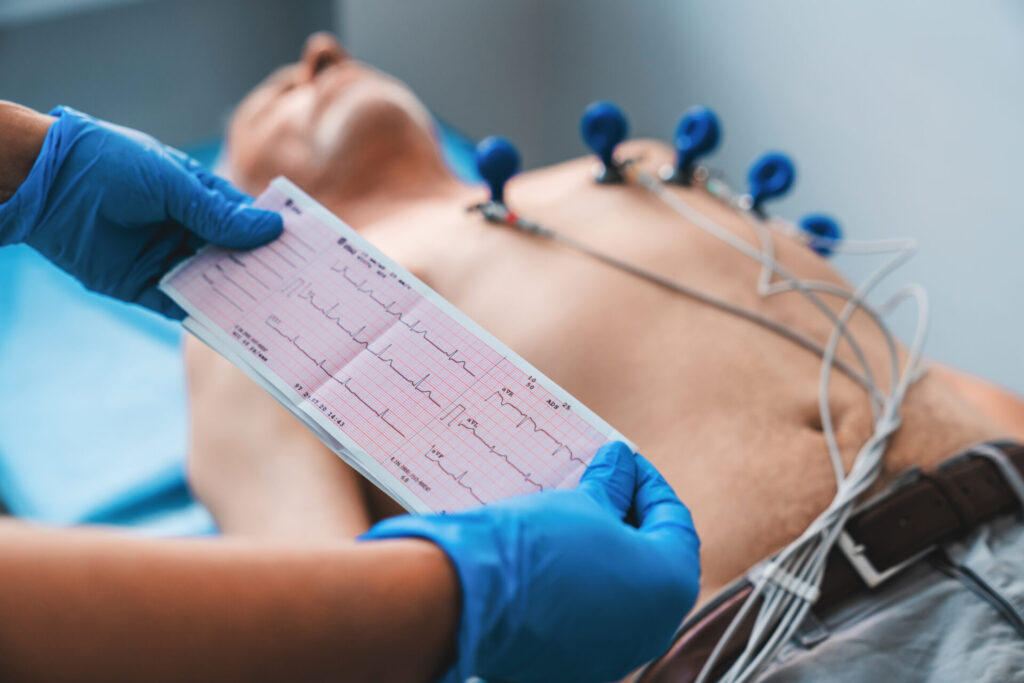
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
What it does:
An ECG records the electrical signals of your heart to detect abnormal rhythms and patterns.
What happens during the test:
You’ll lie down while small sticky electrodes are placed on your chest, arms, and legs. Wires connect these to a machine that records your heart’s electrical activity. It is quick, non-invasive, and completely painless.
How to prepare:
Avoid using lotion or oils on your skin before the test, as they may interfere with electrode placement. Otherwise, no preparation is needed.
What it can diagnose:
Arrhythmias, previous heart attacks, and other electrical abnormalities like atrial fibrillation or heart blocks.

Holter Monitor (24 hr/48 hr/72 hr)
What it does:
A Holter monitor continuously records your heart’s rhythm over 24 to 72 hours to capture irregularities that may not show up during a short ECG.
What happens during the test:
Small electrodes are attached to your chest and connected to a lightweight recording device worn on your belt or shoulder. You’ll go about your normal activities and keep a symptom diary. At the end of the period, you return the device for analysis.
How to prepare:
Wear comfortable clothes. Avoid getting the device wet. You may be asked to avoid magnetic fields or certain electronics. A technician will explain all restrictions.
What it can diagnose:
Intermittent arrhythmias, unexplained dizziness or palpitations, skipped beats, and heart rate abnormalities.

Exercise Stress Test (GXT – Graded Exercise Test)
What it does:
This test evaluates how your heart performs during physical exertion by monitoring ECG, blood pressure, and heart rate as you exercise.
What happens during the test:
You’ll walk on a treadmill while connected to ECG leads. The treadmill’s speed and incline will gradually increase. Your vital signs and symptoms will be monitored throughout. The test is stopped if you feel unwell or reach your maximum target heart rate.
How to prepare:
Avoid eating or drinking for 2 hours before the test. Wear comfortable clothing and walking shoes. Take medications as directed by your doctor.
What it can diagnose:
Blocked coronary arteries (ischemia), exercise-induced arrhythmias, and overall cardiovascular fitness.

Stress Echocardiogram
What it does:
Combines a treadmill or medication-induced stress test with an ultrasound (echocardiogram) to visualize how your heart responds to exertion.
What happens during the test:
An echocardiogram is taken before and immediately after stress is applied through exercise or medication. Gel is applied to your chest, and images are captured with a transducer.
How to prepare:
Avoid caffeine and smoking on the day of the test. Do not eat 2–3 hours before. Wear exercise-appropriate clothing. Follow your doctor’s advice about medications.
What it can diagnose:
Reduced blood flow to parts of the heart (ischemia), wall motion abnormalities, and viability of heart tissue post-heart attack.

Contrast Echocardiogram
What it does:
Enhances the quality of standard echocardiograms using a contrast agent (a safe, injectable solution) to better visualize heart chambers and blood flow.
What happens during the test:
After baseline imaging, a contrast agent is injected into a vein (usually in your arm), and additional ultrasound images are captured. It is safe and minimally invasive.
How to prepare:
Usually, no special preparation is needed. Inform the technician if you have allergies or kidney issues.
What it can diagnose:
Structural heart abnormalities, heart function in technically difficult cases, and better definition of the endocardial border or cardiac masses.

Stress Contrast Echocardiogram
What it does:
Combines stress echocardiography and contrast enhancement to give the most detailed assessment of how your heart performs under stress.
What happens during the test:
You’ll undergo either treadmill exercise or be given a medication to stress the heart. During and after the stress period, contrast-enhanced echocardiogram images are taken to observe the heart in action.
How to prepare:
Similar to a regular stress echo — avoid food, caffeine, and certain medications unless instructed otherwise. Wear comfortable clothing and notify staff of any allergies.
What it can diagnose:
Coronary artery disease, subtle heart wall abnormalities, and heart muscle viability with greater imaging precision.

Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM)
What it does:
Measures and records your blood pressure automatically at regular intervals over 24 hours to track patterns during your normal routine.
What happens during the test:
A cuff is placed on your arm and connected to a small portable monitor. The cuff inflates every 15–30 minutes during the day and hourly at night. You wear the monitor while continuing your normal activities.
How to prepare:
Wear loose-fitting sleeves and go about your normal day. Keep your arm still when the cuff inflates. Avoid excessive movement or high-impact exercise.
What it can diagnose:
Masked hypertension, white coat hypertension, nocturnal blood pressure issues, and response to BP medications.

Holter Monitoring

Ambulatory BP Monitoring

INR Instant Testing

Pulmonary Function Tests


